What is a Wood Screw and How to Choose the Right One for Your Project
In the world of woodworking and construction, understanding the nuances of fastening solutions is crucial. Wood screws, a fundamental element in many DIY and professional projects, come in various types, sizes, and materials. Renowned woodworking expert, John Smith, emphasizes the importance of choosing the right screw for the job, stating, "The right wood screw can make all the difference between a sturdy build and a weak structure." This underscores the idea that not all wood screws are suitable for every application, and selecting the appropriate one can enhance the durability and longevity of your project.
When embarking on a new project, considering the specific requirements—such as the type of wood, the desired strength, and environmental conditions—can greatly influence the performance of your wood screws. From deck building to furniture making, understanding the different features of wood screws can lead to more successful outcomes. This guide will delve into the essential aspects of wood screws, providing insight into their types, usage, and tips on making the right choice tailored to your unique needs. Whether you are a seasoned carpenter or a novice enthusiast, a firm grasp of wood screw selection can elevate your craftsmanship and ensure your creations stand the test of time.

Understanding the Basics of Wood Screws: Definition and Types

Wood screws are essential fasteners widely used in woodworking and construction. At their core, a wood screw consists of a threaded shaft that is designed to be driven into wood materials. They typically feature a pointed tip for easy insertion and a head that enables driving with a tool. The standard materials for wood screws include steel, stainless steel, and brass, each serving distinct applications based on strength, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic needs.
There are various types of wood screws, each tailored for specific projects. Flat head screws, for instance, are designed for flush installation, while round head screws offer a decorative finish. Certain projects may require specialized screws such as deck screws, which have a corrosion-resistant coating for outdoor usage. According to industry reports, the wood screw segment in the global fasteners market is projected to reach a valuation of over $70 billion by 2026, driven by the construction and furniture sectors. Understanding these types can significantly impact the durability and quality of a woodworking project, making the selection process crucial for both amateur and professional craftsmen.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Wood Screws for Your Project
When selecting wood screws for your project, several key factors should be considered to ensure optimal performance and durability. First and foremost, assess the type of wood you are working with. Hardwoods and softwoods have different densities, which affects screw choice. For softer woods, shorter screws with coarse threads might suffice, while harder woods typically require longer screws with finer threads to penetrate effectively. Additionally, the depth of the wood will determine the length of the screw needed to achieve a strong hold without risk of breaking through.
 Another crucial factor is the screw's material and coating. For outdoor projects or areas exposed to moisture, it's essential to choose screws made from corrosion-resistant materials or those that come with protective coatings, such as epoxy or zinc. This feature helps prevent rust and increases the lifespan of the screw. Additionally, consider the drive type of the screw; options like Phillips, square, or Torx can influence torque and ease of use during installation. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can ensure that you select the right wood screws that meet the specific requirements of your project.
Another crucial factor is the screw's material and coating. For outdoor projects or areas exposed to moisture, it's essential to choose screws made from corrosion-resistant materials or those that come with protective coatings, such as epoxy or zinc. This feature helps prevent rust and increases the lifespan of the screw. Additionally, consider the drive type of the screw; options like Phillips, square, or Torx can influence torque and ease of use during installation. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can ensure that you select the right wood screws that meet the specific requirements of your project.
Matching Wood Screw Types to Specific Materials and Applications
When selecting wood screws for specific materials and applications, it's essential to consider the type of wood you are working with. Softwoods, such as pine or cedar, generally require larger, coarse-threaded screws designed to grip the softer fibers effectively. These screws are typically easier to drive in and provide adequate holding power without splitting the wood.
 For hardwoods like oak or maple, finer-threaded screws are recommended, as they can penetrate the denser material more easily, ensuring a secure fit.
For hardwoods like oak or maple, finer-threaded screws are recommended, as they can penetrate the denser material more easily, ensuring a secure fit.
Furthermore, the application plays a crucial role in screw selection. For outdoor projects or areas exposed to moisture, using corrosion-resistant screws is vital to prevent rust and ensure longevity. Conversely, if you are working on indoor furniture, standard steel or brass screws may be suitable.
 Additionally, ensuring the screw length is appropriate for the material thickness is key; a rule of thumb is to use screws that penetrate at least half the thickness of the secondary material being joined. By matching the screw type and features to both the material and specific application, you can enhance the durability and strength of your project.
Additionally, ensuring the screw length is appropriate for the material thickness is key; a rule of thumb is to use screws that penetrate at least half the thickness of the secondary material being joined. By matching the screw type and features to both the material and specific application, you can enhance the durability and strength of your project.
Understanding Screw Sizes, Threads, and Length: A Guide
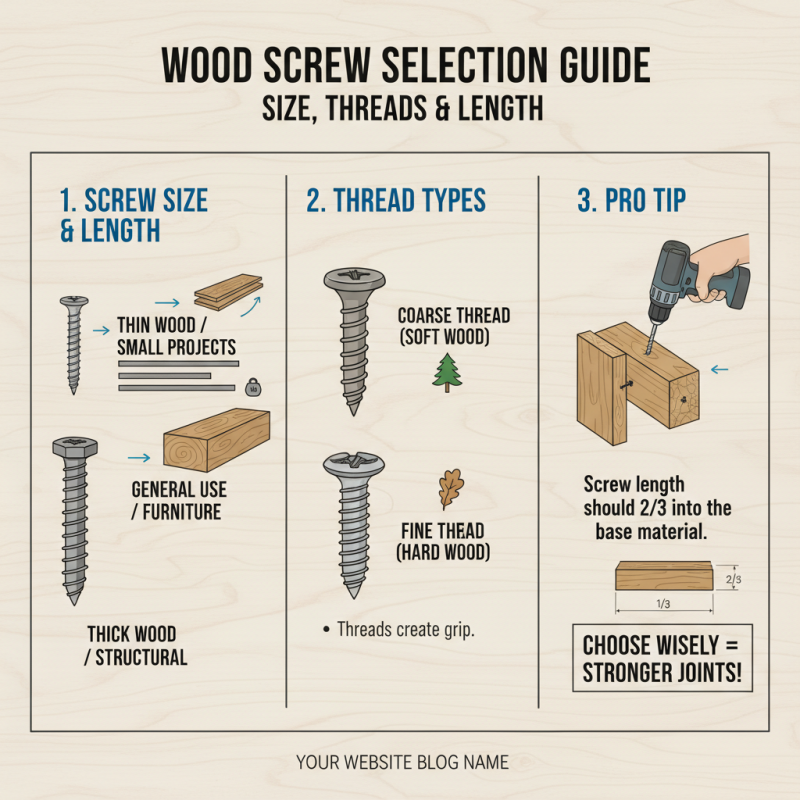
When selecting a wood screw for your project, understanding screw sizes, threads, and lengths is essential. Screw size refers to the diameter and length of the screw, which often determines its load-bearing capacity and suitability for different materials. A good practice is to choose a screw size that is appropriate for the thickness of the wood you are joining. For example, thinner materials typically require smaller screws, while thicker woods can accommodate larger screws.
Threads play a crucial role in how a screw grips into the material. Coarse threads are generally preferred for softwoods, as they provide better holding power and reduce the risk of splitting. In contrast, fine threads are ideal for hardwoods and are also used when a flatter surface is desired as they create a smoother finish. Additionally, the length of the screw should be chosen not only based on the material thickness but also on the design of the joint. A good rule of thumb is to ensure that at least half of the screw's length penetrates the second piece of wood to achieve a strong joint without compromising stability. By considering these factors, you can select the right wood screw that meets the needs of your project effectively.
Best Practices for Installing and Using Wood Screws Effectively
When it comes to installing wood screws, proper technique is crucial for achieving strong and lasting connections. Begin by selecting the right drill bit size for pilot holes; a pilot hole helps prevent the wood from splitting and ensures that the screw goes in smoothly. It’s advisable to use a bit that is slightly smaller than the screw’s diameter, allowing the threads to grip the wood effectively without excessive resistance. Ensuring that the screw is centered in both the pilot hole and the wood piece will provide better stability and alignment during installation.
Additionally, the choice of screwdriver or drill settings can greatly impact the outcome. Using the appropriate torque settings on a power drill helps to prevent overdriving the screw, which can strip the hole or damage the wood. If you are working with softer woods, it's important to monitor the pressure applied while driving the screw, as too much force can lead to stripping. When fastening multiple screws in succession, consider working from the center outwards or in a diagonal pattern to distribute stress evenly and maintain the structural integrity of the project. Following these best practices will enhance both the efficiency of your work and the durability of your final assembly.
What is a Wood Screw and How to Choose the Right One for Your Project - Best Practices for Installing and Using Wood Screws Effectively
| Feature | Description | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Typically made of steel, stainless steel, or brass. | General wood projects, outdoor woodworking (stainless steel). |
| Head Type | Common types include flat, round, and pan heads. | Visible joints, countersunk applications. |
| Drive Type | Phillips, slotted, Torx, or hex drives. | Personal preference, torque requirements. |
| Length | Available in various lengths, typically 1" to 6". | Thickness of the material being joined. |
| Diameter | Commonly measured in gauges (e.g., #6, #8, #10). | Strength and load-bearing needs. |
| Thread Type | Fine threads for hard woods, coarse threads for soft woods. | Type of wood being used. |
Related Posts
-

How to Use Torx Screws for Effective and Secure Fastening Solutions
-

Top 2025 Furniture Screw Types: Which One is Right for Your Project?
-

What is a Stainless Wood Screw and How to Choose the Right One?
-

How to Choose the Right Furniture Screw for Your DIY Projects
-

Why You Need High Quality Carriage Bolts for Your DIY Projects
